1776 electric box japan The Museum has been designed to enable visitors to trace the 120-year history of the Japanese electric power industry, which has always focused on securing a stable supply of electric . CNC manufacturing emerged in the 1940s and has evolved into fully digitized, computer-operated production systems used by CNC production companies.
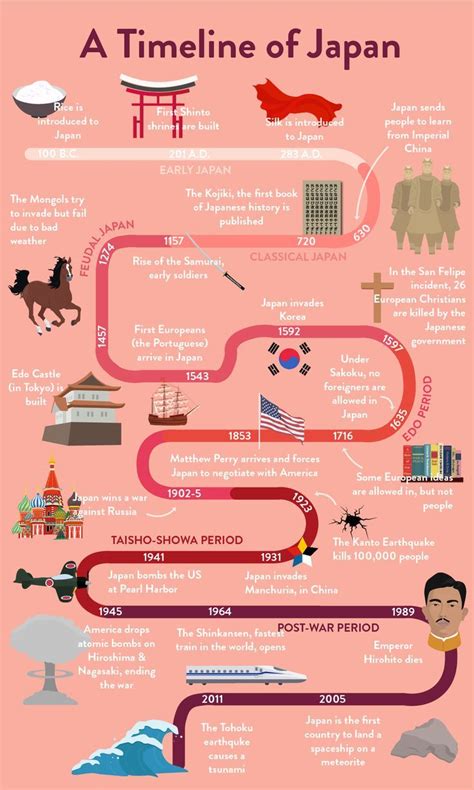
0 · Timeline of Japanese history
1 · TEPCO : Electric Power Historical Museum
2 · Modern Toys Spirit of 1776 Train Tin Litho Made in Japan WITH
3 · Milestone
4 · History of Japan’s Electric Utility Industry
5 · History of Japan's Electric Power Industry
6 · Formation of Electrical Machinery Technology in the Edo Period
7 · Elekiter
8 · An Early Episode in the History of Electrotherapy in Japan
Patented Lenco alloy wheel repair machinery capable of precision diamond cutting wheel repairs, rim straightening, mag polishing and alloy wheel refinishing.
Timeline of Japanese history
The Elekiter (エレキテル, Erekiteru, derived from Dutch elektriciteit, for electricity) is the Japanese name for a type of generator of static electricity used for electric experiments in the 18th century. In Japan, Hiraga Gennai presented his own elekiter in 1776, derived from an elekiter from Holland. The elekiter consists of a small box that uses the power of friction to generate electricity and store it.
In 1776, a friction-induced electrostatic generator was first demonstrated in Japan by Gennai Hiraga after he spent six years repairing and restoring a broken device imported from the Netherlands. Six year later, in 1776, he was the first person in Japan to produce electricity (electric charge). Gennai is called the “father of electricity,” but he conducted his experiments . As a result, European natural science made its way into Japan, opening the way for the formation of electrical machinery technology. This paper describes electrical machinery .
metal piece in iphone 12 box
TEPCO : Electric Power Historical Museum
The Museum has been designed to enable visitors to trace the 120-year history of the Japanese electric power industry, which has always focused on securing a stable supply of electric .
The earliest description of an electrical appliance, known in Japanese as erekiteru, can be found in the 1765 work of Gotō Rishun, Oranda banashi or Stories of Holland, which also contains .After the end of the second World War in 1945, supply and demand for electricity remained very tight in Japan. A series of intense discussions were held on restructuring the electric utility . unfamiliar and uncommon not only in Japan but also in Europe and the United States. In 1886, Tokyo Electric Lighting, a private company, commenced operations as the .Japan quickly transformed in one generation from an isolated feudal society to a modern industrialized nation state and an emerging great power. 1876: Akizuki, Hagi and Shinpūren .
This Modern Toys Spirit of 1776 Train Tin Litho, made in Japan, is a vintage piece that will surely spark collectors' interest. The intricate details of the train litho, coupled with its original box, .
In Japan, Hiraga Gennai presented his own elekiter in 1776, derived from an elekiter from Holland. The elekiter consists of a small box that uses the power of friction to generate electricity and store it.In 1776, a friction-induced electrostatic generator was first demonstrated in Japan by Gennai Hiraga after he spent six years repairing and restoring a broken device imported from the Netherlands. Six year later, in 1776, he was the first person in Japan to produce electricity (electric charge). Gennai is called the “father of electricity,” but he conducted his experiments as late as 100 years after von Guericke's experiments with the sulfur globe.
As a result, European natural science made its way into Japan, opening the way for the formation of electrical machinery technology. This paper describes electrical machinery technology in Japan in comparison with that of Western Europe at the time of the Edo period.The Museum has been designed to enable visitors to trace the 120-year history of the Japanese electric power industry, which has always focused on securing a stable supply of electric power for Japan as well as caring for the environment.The earliest description of an electrical appliance, known in Japanese as erekiteru, can be found in the 1765 work of Gotō Rishun, Oranda banashi or Stories of Holland, which also contains references to its use in the treatment of diseases.
metal planter boxes auckland
After the end of the second World War in 1945, supply and demand for electricity remained very tight in Japan. A series of intense discussions were held on restructuring the electric utility industry as one of the measures for democratizing the economy.
unfamiliar and uncommon not only in Japan but also in Europe and the United States. In 1886, Tokyo Electric Lighting, a private company, commenced operations as the nation’s first electric power company, and began supplying .
Japan quickly transformed in one generation from an isolated feudal society to a modern industrialized nation state and an emerging great power. 1876: Akizuki, Hagi and Shinpūren Rebellions. 1877: Satsuma Rebellion. 1878: 23 August: Takebashi incident: A riot by underpaid Imperial Guards. 1884: Chichibu incident: A peasants rebellion. 1890: 29 .
This Modern Toys Spirit of 1776 Train Tin Litho, made in Japan, is a vintage piece that will surely spark collectors' interest. The intricate details of the train litho, coupled with its original box, make it a valuable addition to any collection. Very good condition for its age. Please take a look at the pictures, and feel free to ask me any .In Japan, Hiraga Gennai presented his own elekiter in 1776, derived from an elekiter from Holland. The elekiter consists of a small box that uses the power of friction to generate electricity and store it.In 1776, a friction-induced electrostatic generator was first demonstrated in Japan by Gennai Hiraga after he spent six years repairing and restoring a broken device imported from the Netherlands. Six year later, in 1776, he was the first person in Japan to produce electricity (electric charge). Gennai is called the “father of electricity,” but he conducted his experiments as late as 100 years after von Guericke's experiments with the sulfur globe.
As a result, European natural science made its way into Japan, opening the way for the formation of electrical machinery technology. This paper describes electrical machinery technology in Japan in comparison with that of Western Europe at the time of the Edo period.The Museum has been designed to enable visitors to trace the 120-year history of the Japanese electric power industry, which has always focused on securing a stable supply of electric power for Japan as well as caring for the environment.
The earliest description of an electrical appliance, known in Japanese as erekiteru, can be found in the 1765 work of Gotō Rishun, Oranda banashi or Stories of Holland, which also contains references to its use in the treatment of diseases.After the end of the second World War in 1945, supply and demand for electricity remained very tight in Japan. A series of intense discussions were held on restructuring the electric utility industry as one of the measures for democratizing the economy. unfamiliar and uncommon not only in Japan but also in Europe and the United States. In 1886, Tokyo Electric Lighting, a private company, commenced operations as the nation’s first electric power company, and began supplying .
Japan quickly transformed in one generation from an isolated feudal society to a modern industrialized nation state and an emerging great power. 1876: Akizuki, Hagi and Shinpūren Rebellions. 1877: Satsuma Rebellion. 1878: 23 August: Takebashi incident: A riot by underpaid Imperial Guards. 1884: Chichibu incident: A peasants rebellion. 1890: 29 .
Modern Toys Spirit of 1776 Train Tin Litho Made in Japan WITH

Shop for steel sheet at America's Metal Superstore. Largest selection of Hot Rolled Steel Sheet, Cold Rolled Steel Sheet, Galvanized Steel Sheet at wholesale prices. Any Quantity, Any Size, Delivered Anywhere!
1776 electric box japan|History of Japan's Electric Power Industry