3d box beam distributed load problem Problem 590 A box beam carries a distributed load of 200 lb/ft and a concentrated load P as shown in Fig. P-590. Determine the maximum value of P if f b ≤ 1200 psi and f v ≤ 150 psi. In the event that you don’t have a wood screw, you can use sheet metal screws to complete your woodworking task. If you pick the right size, shape (flat head), and shank thickness, a sheet metal screw may be used for many wood projects.
0 · distributed loads on beams
1 · distributed loads linear action
2 · distributed loads integration
3 · distributed loads explained
4 · distributed loads diagram
5 · distributed load properties diagram
6 · distributed load properties
7 · distributed load model
U.S. Sheet Metal Company, Inc.. "Custom metal fabrication of range hoods, countertops, sinks, backsplashes, fireplace surrounds, railing systems, copper roofing.
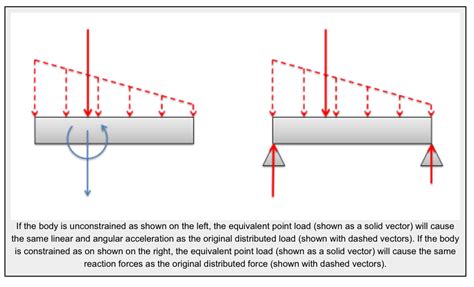
To use a distributed load in an equilibrium problem, you must know the equivalent magnitude to sum the forces, and also know the position or line of action to sum the moments. The line of action of the equivalent force acts through the .Problem 590 A box beam carries a distributed load of 200 lb/ft and a concentrated load P as shown in Fig. P-590. Determine the maximum value of P if f b ≤ 1200 psi and f v ≤ 150 psi.8.4 - A triangular distributed load is acting downward on a simply supported beam. Determine the reaction forces. 8.5 - This simply supported beam has a composite distribute load (rectangular and parabolic). Determine the reaction .Find the deflected shape of the beam using the direct integration method. Find the maximum deflection magnitude and location. Determine the location and magnitude of the maximum .
distributed loads on beams
distributed loads linear action
To use a distributed load in an equilibrium problem, you must know the equivalent magnitude to sum the forces, and also know the position or line of action to sum the moments. The line of action of the equivalent force acts through the .moments. Consequently, it is often necessary to replace a pressure or distributed load with a single force. First, consider a simple example. We will apply a uniform load to a beam that is 3 .The distributed load shown in Fig. P-586 is supported by a box beam having the same cross-section as that in Prob. 585. Determine the maximum value of w o that will not exceed a .
A 3D beam with rectangular distributed loading is supported by two cables and a ball and socket joint. See the sketch for details. Answer the following: (a) Replace the distributed load with an .
Distributed Loads Decimals have a point Distributed Loads ! Up to this point, all the forces we have . So here it would be the load intensity time the beam length. 8 Distrubuted Loads .To use a distributed load in an equilibrium problem, you must know the equivalent magnitude to sum the forces, and also know the position or line of action to sum the moments. The line of action of the equivalent force acts through the centroid of area under the load intensity curve.Problem 590 A box beam carries a distributed load of 200 lb/ft and a concentrated load P as shown in Fig. P-590. Determine the maximum value of P if f b ≤ 1200 psi and f v ≤ 150 psi.
benchmill 6000 cnc machining center
distributed loads integration

bell weatherproof junction boxes
8.4 - A triangular distributed load is acting downward on a simply supported beam. Determine the reaction forces. 8.5 - This simply supported beam has a composite distribute load (rectangular and parabolic). Determine the reaction forces.Distributed loads are a way to represent a force over a certain distance. Sometimes called intensity, given the variable: Intensity w = F / d [=] N/m, lb/ft. While pressure is force over area (for 3d problems), intensity is force over distance (for 2d problems). It’s like a bunch of mattresses on the back of a truck.Find the deflected shape of the beam using the direct integration method. Find the maximum deflection magnitude and location. Determine the location and magnitude of the maximum stress in the beam. Calculate the second moment of inertia of the beam cross section for: Solid rectangular cross section of width b and height h.To use a distributed load in an equilibrium problem, you must know the equivalent magnitude to sum the forces, and also know the position or line of action to sum the moments. The line of action of the equivalent force acts through the centroid of area under the load intensity curve.
moments. Consequently, it is often necessary to replace a pressure or distributed load with a single force. First, consider a simple example. We will apply a uniform load to a beam that is 3 m long and the space, abetween the wall and the beginning of the applied load is 0.5 m.
The distributed load shown in Fig. P-586 is supported by a box beam having the same cross-section as that in Prob. 585. Determine the maximum value of w o that will not exceed a flexural stress of 10 MPa or a shearing stress of 1.0 MPa.A 3D beam with rectangular distributed loading is supported by two cables and a ball and socket joint. See the sketch for details. Answer the following: (a) Replace the distributed load with an equivalent single force.Distributed Loads Decimals have a point Distributed Loads ! Up to this point, all the forces we have . So here it would be the load intensity time the beam length. 8 Distrubuted Loads Monday, November 5, 2012 . 5 . Example Problem ! Break the load into a rectangular load and a triangular load 5 ft 4 ft A B 100 lb/ft 100 lb/ft A y A x B y. 15
To use a distributed load in an equilibrium problem, you must know the equivalent magnitude to sum the forces, and also know the position or line of action to sum the moments. The line of action of the equivalent force acts through the centroid of area under the load intensity curve.Problem 590 A box beam carries a distributed load of 200 lb/ft and a concentrated load P as shown in Fig. P-590. Determine the maximum value of P if f b ≤ 1200 psi and f v ≤ 150 psi.8.4 - A triangular distributed load is acting downward on a simply supported beam. Determine the reaction forces. 8.5 - This simply supported beam has a composite distribute load (rectangular and parabolic). Determine the reaction forces.
distributed loads explained
Distributed loads are a way to represent a force over a certain distance. Sometimes called intensity, given the variable: Intensity w = F / d [=] N/m, lb/ft. While pressure is force over area (for 3d problems), intensity is force over distance (for 2d problems). It’s like a bunch of mattresses on the back of a truck.
Find the deflected shape of the beam using the direct integration method. Find the maximum deflection magnitude and location. Determine the location and magnitude of the maximum stress in the beam. Calculate the second moment of inertia of the beam cross section for: Solid rectangular cross section of width b and height h.
To use a distributed load in an equilibrium problem, you must know the equivalent magnitude to sum the forces, and also know the position or line of action to sum the moments. The line of action of the equivalent force acts through the centroid of area under the load intensity curve.
moments. Consequently, it is often necessary to replace a pressure or distributed load with a single force. First, consider a simple example. We will apply a uniform load to a beam that is 3 m long and the space, abetween the wall and the beginning of the applied load is 0.5 m.The distributed load shown in Fig. P-586 is supported by a box beam having the same cross-section as that in Prob. 585. Determine the maximum value of w o that will not exceed a flexural stress of 10 MPa or a shearing stress of 1.0 MPa.A 3D beam with rectangular distributed loading is supported by two cables and a ball and socket joint. See the sketch for details. Answer the following: (a) Replace the distributed load with an equivalent single force.
bellwood sheet metal
Remove old outlet from old box, then use wire nuts to tie the wires in that now-empty box (A) to NEW wire going to a new box (B) Leave the old box (A) as a junction box - just wires tied together -- and cover with an ordinary .
3d box beam distributed load problem|distributed load properties