comparing distributions of box plots Here we will learn about a box plot, including how to draw a box plot to represent a set of data, how to read data from a box plot, and how to interpret and compare box plots. There are also box plot worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and .
This junction box will allow function (or power) wires to be tied together to customize your DOT system. not mayIMPORTANT! Do mount the Junction Box where it be exposed to moisture. The passenger compartment is the recommended mounting location. (+) Battery (-)
0 · side by boxplot interpretation
1 · matlab boxplot vs box chart
2 · how to solve box plots
3 · comparing box plots worksheet pdf
4 · comparing box plots worksheet
5 · comparing box plots problems
6 · comparing box plots and histograms
7 · comparing box and whisker plots
A junction box – also known as an ‘electrical box’, ‘jbox’, ‘or ‘terminal box’ – is a protective box where wires are interconnected. Junction boxes are often built into the plaster of a wall, in the ceiling, or within concrete.
When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median .
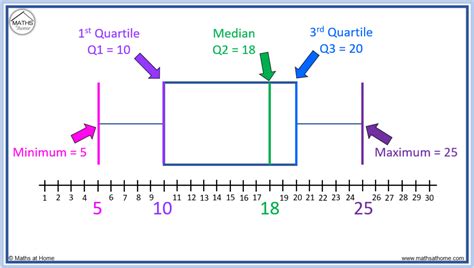
Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the .
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
Box plots are useful because they allow us to gain a quick understanding of the distribution of values in a dataset. They’re also useful for comparing two different datasets. When comparing two or more box plots, we .
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum .
Here we will learn about a box plot, including how to draw a box plot to represent a set of data, how to read data from a box plot, and how to interpret and compare box plots. There are also box plot worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and . This post describes box plots and shows their advantages. Box plots, also called box and whisker plots, are more useful than histograms for comparing distributions. In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.compare two data sets given their cumulative frequency diagrams on the same grid. In this lesson, we will learn how to compare distributions of multiple data sets using their statistics as well as their visual representations.
When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize differences among groups that have been measured on the same variable.Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the positions of the median and the quartiles.
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. Box plots are useful because they allow us to gain a quick understanding of the distribution of values in a dataset. They’re also useful for comparing two different datasets. When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.Here we will learn about a box plot, including how to draw a box plot to represent a set of data, how to read data from a box plot, and how to interpret and compare box plots. There are also box plot worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
This post describes box plots and shows their advantages. Box plots, also called box and whisker plots, are more useful than histograms for comparing distributions.
custom small parts metal furniture
In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.
compare two data sets given their cumulative frequency diagrams on the same grid. In this lesson, we will learn how to compare distributions of multiple data sets using their statistics as well as their visual representations. When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?
side by boxplot interpretation
In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize differences among groups that have been measured on the same variable.Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the positions of the median and the quartiles.A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
Box plots are useful because they allow us to gain a quick understanding of the distribution of values in a dataset. They’re also useful for comparing two different datasets. When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.Here we will learn about a box plot, including how to draw a box plot to represent a set of data, how to read data from a box plot, and how to interpret and compare box plots. There are also box plot worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck. This post describes box plots and shows their advantages. Box plots, also called box and whisker plots, are more useful than histograms for comparing distributions.
In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.
matlab boxplot vs box chart
how to solve box plots
These plain metal lunch boxes reflect your sleek sense of style, as well as the fluorescent lights of the lunch room. These are perfect for anyone who wishes to customize a lunchbox - with their own sense of style or with a private logo.
comparing distributions of box plots|comparing box plots worksheet pdf