transition metal orbital box diagram 1.3 Transition Metals. Electronic Configuration of Transition Metals. d-block transition metals have an incomplete d-subshell in at least one of their ions. 4s electrons are lost before 3d electrons . Wayland Sheet Metal & Fabrications Ltd is a well established manufacturing company that specialises in providing a quality sheet metal fabrication service from start to finish, including the initial consultation through to delivery.
0 · transition metal cations diagram
1 · orbital transitions chemistry
2 · orbital electron structure diagram
3 · orbital electron configuration diagram
4 · orbital diagram of transition metals
5 · orbital diagram of metal cations
6 · electronic structure of transition metals pdf
7 · electronic configuration of transition metals
Shop SentrySafe 0.8-cu ft Fireproof and Waterproof Home Safe with Electronic/Keypad Lock in the Floor & Wall Safes department at Lowe's.com. The SentrySafe SFW082F fireproof safe and waterproof safe provides powerful protection for your home or office security needs.
In the ground state, the electron configuration of the transition metals follows the format, ns 2 nd x. As for the electron configuration for transition metals that are charged (i.e. Cu +), the electrons from the s orbital will be .When we get to period 4-7 on the periodic table, we will require the use of the d and f orbitals for transition metals and inner transition metals. Let's take a look at a few examples on how to write the electron configuration for such elements.Learning Objectives. To write the electron configuration of the transition metals. To understand the basis for the exceptions to the normal order of filling.. Now you can use the information you learned in Section 2.5 to determine the electronic .1.3 Transition Metals. Electronic Configuration of Transition Metals. d-block transition metals have an incomplete d-subshell in at least one of their ions. 4s electrons are lost before 3d electrons .
Transition elements or transition metals. These are metallic elements in which the last electron added enters a d orbital. The valence electrons (those added after the last noble gas configuration) in these elements include the ns and ( n – 1) .The electron configurations and orbital box diagrams of these four elements are: The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. This electron must go into the lowest-energy subshell available, the 3s .
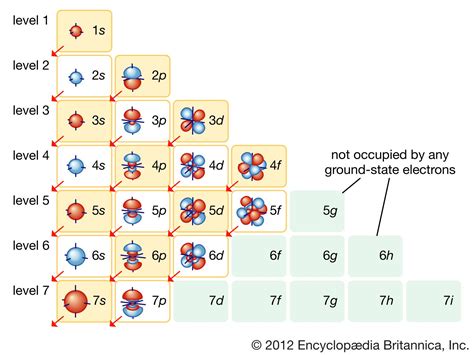
Electron configurations and orbital box diagrams. We will now construct the ground-state electron configuration for a selection of atoms in the first and second periods. Next, we will create the corresponding orbital box diagram (also .The periodic table can be divided into three categories based on the orbital in which the last electron to be added is placed: main group elements (s and p orbitals), transition elements (d orbitals), and inner transition elements (f orbitals). Transition elements or transition metals. These are metallic elements in which the last electron added enters a d orbital. The valence electrons (those added after the last noble gas configuration) in these .In this article, we will explore the orbital box diagram for iron, a transition metal with the atomic number 26. Iron is located in the 4th period and belongs to the d-block of the periodic table. It has an atomic configuration of 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6 .
Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds 3h 16m. Worksheet. Atomic Radius & Density of Transition Metals. 11m. . What does each box in an orbital diagram represent? Verified Solution. This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above. Video duration: 5m. Play a video:The periodic table can be a powerful tool in predicting the electron configuration of an element. However, we do find exceptions to the order of filling of orbitals that are shown in Figure 4.1.3 or Figure 4.1.4.For instance, the electron . The Aufbau principle predicts that the 4s orbital is always filled before the 3d orbitals, but this is actually not true for most elements! From Sc on, the 3.-O THE TRANSITION METALS Drawing a crystal field theory energy level diagram [MoBr4 complex Using crystal field theory, draw an electron box energy level diagram for the valence d orbitals on the molybdenum atom in a tetrahedral Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electrons in each orbital Note: to make your diagram easier .
Electron Configuration Exceptions. The periodic table can be a powerful tool in predicting the electron configuration of an element. However, we do find exceptions to the order of filling of orbitals shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.For instance, the electron configurations (shown in Figure 6) of the transition metals chromium (Cr; atomic number 24) and copper (Cu; atomic number .
transition metal cations diagram

orbital transitions chemistry
The d orbital splitting diagram is shown in a box. Suppose the diagram above is for a first row transition metal. The diagram for a second or third row metal is similar, but with stronger bonds. If the bonding interaction is stronger between the metal and ligand, then so is the antibonding interaction. The antibonding levels are bumped higher .For orbital box diagrams, this means two arrows go in each box, representing two electrons in each orbital. The arrows must point in opposite directions (representing paired spins). The electron configuration and orbital box diagram of helium are: . Starting with the transition metal scandium (atomic number 21), we add electrons successively .
Consider the transition metal complex, K 3 [Fe(CN) 6]. (i) Define the term ligand, and identify the ligand in this complex. (1) (ii) Write the full electron configuration and draw the orbital box diagram of iron in its oxidation state in this complex, and hence, determine the number of unpaired electrons in this state. (3)
Question: (e) In the molecular orbital diagram of an octahedral transition metal complex with sigma-only donor ligands, which orbitals constitute to frontier molecular orbitals (i.e., designated inside a box in the MO diagram)?(f) Write down the orbital sets that constitute the frontier molecular orbitals of a metallocene complex (i.e., those enclosed in a box onDownload scientific diagram | (Color online) The d-orbital energy splittings of a transition metal surrounded by oxygen ligands in (a) regular octahedral CEF in O h symmetry, (b) octahedral CEF . This book starts with the most elementary ideas of molecular orbital theory and leads the reader progressively to an understanding of the electronic structure, geometry and, in some cases, reactivity of transition metal complexes. The qualitative orbital approach, based on simple notions such as symmetry, overlap and electronegativity, is the .
According to the aufbau principle the 4s orbital is lower in energy than the 3d orbital hence, it is filled first. However, when we consider a transition metal complex this does not apply; the 3d .Here is a schematic orbital box diagram for a hydrogen atom in its ground state: . Electron Configuration of Transition Metals and Inner Transition Metals . So far, we have studied the electron configuration for elements in periods 1-3 on the .Question: *molecular orbital diagram for a transition metal complex* A)Circle non binding molecular orbitals in this diagram. Which Ligand or metal orbitals contribute most to these non binding orbitals? B) put a rectangular box around .
An orbital box diagram can be written as well. Boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin–one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing .Orbital Diagram for Cd2+ Cadmium (Cd) is a transition metal with an atomic number of 48. When Cd loses two electrons to form Cd2+, it becomes a cation with a +2 charge. The orbital diagram for Cd2+ illustrates how the electrons are distributed in the orbitals of the ion. In the ground state of Cd2+, the electronic configuration is [Kr]4d10.The d orbital splitting diagram is a pictorial representation that illustrates how the five d orbitals of a transition metal ion split into different energy levels in the presence of surrounding ligands. . The d orbital splitting diagram is important in square planar geometry because it helps us determine the electronic configuration and the .
Write the electron configuration and orbital box diagrams for each of the following transition metal ions. Indicate which ion is the most paramagnetic? (a) C (b) Co (c) Co- (d) Fe (e) Fe Cu . Show transcribed image text. Here’s the best way to solve it. We can use the d-orbital energy-level diagram in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) to predict electronic structures and some of the properties of transition-metal complexes. We start with the Ti 3 + ion, which contains a single d electron, and proceed across the first row of the transition metals by adding a single electron at a time. We place .Question: -O THE TRANSITION METALS -Drawing a crystal field theory energy level diagram using crystal field theory, draw an electron box energy level diagram for the valence d orbitals on the titanium atom in a tetrahedral [Ti diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electrons in each orbital complex.One can slightly modify the model to accomodate complexes of metals which are not transition metal ions. These would not have d valence electrons and only s and p electrons can be used in constructing the molecular orbital energy diagram. Fewer metal orbitals results in fewer interactions between the ligand and the metal ion.
Orbital Diagram Of S: . ions for Ist series of transition metals Orgel and Tanabe Sugano diagrams for transition metal complexes d1 d9 states . uncertainty principle Pictorial representation of the wave equation of a particle in one dimensional box and its influence on
The metal's electronic energy levels are shown on the other side. The result of their interaction, a metal-ligand complex, is shown in the middle. The d orbital splitting diagram is shown in a box. Suppose the diagram above is for a first row transition metal. The diagram for a second or third row metal is similar, but with stronger bonds.This video is on how to write the ground state electronic configuration for the transition metal ions. We look at the promotion from the s orbitals to the d .Question: Examine the d-orbital splitting diagram shown below. Which transition metal complex has the same arrangement of d-orbitals and d-electrons as shown in the diagram? 1 1 eg 11 1. t2g Select one: K[(Ni(en),CL) Ca [Fe(Br [Cr(H20),(NO2)2]CI Na [CO(NH4) [Ni(H20)]ci, . Examine the d-orbital splitting diagram shown below. Which transition .For main group elements, the electrons that were added last are the first electrons removed. For transition metals and inner transition metals, however, electrons in the s orbital are easier to remove than the d or f electrons, and so the highest ns electrons are lost, and then the (n – 1)d or (n – 2)f electrons are removed. An anion .

orbital electron structure diagram

ge electric panel boxes
Isn't this just what you do every time you pick up a piece of sheet metal? I thought it's a requirement just like clicking the tongs together. 100% a requirement. It's in the job description and everything. Source: I build HVAC .
transition metal orbital box diagram|orbital electron configuration diagram