best coolants for cnc machines In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of coolants available, their features, and the factors to consider when choosing the best coolant for CNC machines. Table .
Our pipe twin u-PVC extrusion technology from Theysohn with full automation optimises productivity and quality of the conduits. Fittings are produced with Engel machines, acknowledged to be among the best world-wide, using high performance uPVC compounds.
0 · mist coolant system for cnc
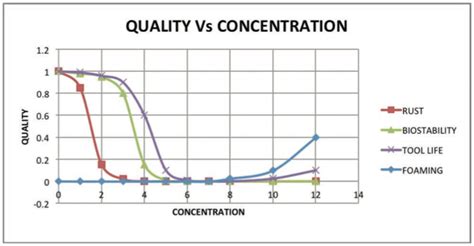
1 · machine coolant concentration chart
2 · lubricant used in cnc machine
3 · coolant system for milling machine
4 · coolant mixers for cnc equipment
5 · coolant concentration for machining
6 · coolant concentration for cnc machines
7 · best semi synthetic machine coolant
Our specialist precision sheet metal work capabilities allow us to manufacture .
mist coolant system for cnc
Make the best choice for your CNC machine by selecting a coolant that is reliable, efficient, and specifically formulated for the demands of machining processes. Opting for top-rated coolants will undoubtedly contribute to the smooth functioning and longevity of your CNC . Selecting the right CNC coolant is crucial for top machining performance. Coolants impact tool life, efficiency, and fluid consumption by reducing heat, friction, and debris. Oil-based, water-based, and synthetic .

punching machine for sheet metal
This article provides a comprehensive look at the types of CNC machine tool coolants available, their uses across industries, the importance of selecting the right coolant, . Soluble oils are among the most commonly used coolants in CNC machining. They are essentially mineral oils that are diluted with water to form an emulsion. Why Use Soluble Oils? Cooling and Lubrication: Soluble oils . By considering these best practices and performance criteria, you can confidently select the ideal CNC coolant for your specific machining requirements, promoting efficiency, longevity, and environmental sustainability.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of coolants available, their features, and the factors to consider when choosing the best coolant for CNC machines. Table . Coolants can be broadly classified into several categories, each with distinct properties and applications: 1. Water-Based Coolants. Example: A water-based coolant .
Virtually all CNC machining centers and lathes today are designed to use water-based fluids, but most Swiss-style screw machines use straight oil. There are three categories of coolants that sometimes overlap: soluble oils, . Learn how to choose the right coolant for your CNC machining needs. Discover the importance of selecting a coolant with anti-foaming properties, consulting with suppliers, and . Make the best choice for your CNC machine by selecting a coolant that is reliable, efficient, and specifically formulated for the demands of machining processes. Opting for top-rated coolants will undoubtedly contribute to the smooth functioning and longevity of .
Selecting the right CNC coolant is crucial for top machining performance. Coolants impact tool life, efficiency, and fluid consumption by reducing heat, friction, and debris. Oil-based, water-based, and synthetic coolants offer varying benefits. No matter what type of CNC machining you do, CNC coolants play a critical role. They help increase tool life and offer a better surface finish on the machined parts. By understanding the available coolant types, you can select a . This article provides a comprehensive look at the types of CNC machine tool coolants available, their uses across industries, the importance of selecting the right coolant, and the factors to consider when choosing the best coolant for CNC machining. Soluble oils are among the most commonly used coolants in CNC machining. They are essentially mineral oils that are diluted with water to form an emulsion. Why Use Soluble Oils? Cooling and Lubrication: Soluble oils provide a balance between cooling and lubrication.
By considering these best practices and performance criteria, you can confidently select the ideal CNC coolant for your specific machining requirements, promoting efficiency, longevity, and environmental sustainability.In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of coolants available, their features, and the factors to consider when choosing the best coolant for CNC machines. Table of Contents: 1. Importance of Coolants in CNC Machines. 2. Types of Coolants\ a. Water-Based Coolants\ b. Synthetic Coolants\ c. Semi-Synthetic Coolants. 3. Coolants can be broadly classified into several categories, each with distinct properties and applications: 1. Water-Based Coolants. Example: A water-based coolant containing rust inhibitors and biocides is used for milling aluminum parts on . Virtually all CNC machining centers and lathes today are designed to use water-based fluids, but most Swiss-style screw machines use straight oil. There are three categories of coolants that sometimes overlap: soluble oils, synthetic fluids and semisynthetic fluids.
Learn how to choose the right coolant for your CNC machining needs. Discover the importance of selecting a coolant with anti-foaming properties, consulting with suppliers, and testing before full implementation for optimal machining performance. Make the best choice for your CNC machine by selecting a coolant that is reliable, efficient, and specifically formulated for the demands of machining processes. Opting for top-rated coolants will undoubtedly contribute to the smooth functioning and longevity of . Selecting the right CNC coolant is crucial for top machining performance. Coolants impact tool life, efficiency, and fluid consumption by reducing heat, friction, and debris. Oil-based, water-based, and synthetic coolants offer varying benefits.
No matter what type of CNC machining you do, CNC coolants play a critical role. They help increase tool life and offer a better surface finish on the machined parts. By understanding the available coolant types, you can select a . This article provides a comprehensive look at the types of CNC machine tool coolants available, their uses across industries, the importance of selecting the right coolant, and the factors to consider when choosing the best coolant for CNC machining. Soluble oils are among the most commonly used coolants in CNC machining. They are essentially mineral oils that are diluted with water to form an emulsion. Why Use Soluble Oils? Cooling and Lubrication: Soluble oils provide a balance between cooling and lubrication. By considering these best practices and performance criteria, you can confidently select the ideal CNC coolant for your specific machining requirements, promoting efficiency, longevity, and environmental sustainability.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of coolants available, their features, and the factors to consider when choosing the best coolant for CNC machines. Table of Contents: 1. Importance of Coolants in CNC Machines. 2. Types of Coolants\ a. Water-Based Coolants\ b. Synthetic Coolants\ c. Semi-Synthetic Coolants. 3. Coolants can be broadly classified into several categories, each with distinct properties and applications: 1. Water-Based Coolants. Example: A water-based coolant containing rust inhibitors and biocides is used for milling aluminum parts on . Virtually all CNC machining centers and lathes today are designed to use water-based fluids, but most Swiss-style screw machines use straight oil. There are three categories of coolants that sometimes overlap: soluble oils, synthetic fluids and semisynthetic fluids.
machine coolant concentration chart
lubricant used in cnc machine
public image metal box discogs
coolant system for milling machine
Typical welding symbols used with sheet metal are shown on a sample part in the diagram. A variety of corners are also shown. These are just a few of the many welding symbols established by the American Welding Society. To reduce errors we prefer to do our own sheet metal bend calculations. When metal is bent it stretches.
best coolants for cnc machines|coolant concentration for machining