frequency distribution box plot Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median . Our expert machinists can manufacture precision CNC Motorcycle Parts for the motorcycle global marketplace as well as the motorcycle repair, motorcycle parts replacement, new motorcycle prototype design and production, motorcycle market prototype and off-road industry, and more.
0 · what is ungrouped frequency distribution
1 · types of frequency distribution tables
2 · types of frequency distribution graphs
3 · types of frequency charts
4 · parts of frequency distribution table
5 · frequency distribution vs relative
6 · frequency distribution graph example
7 · calculating frequency distribution
Our Steel inventory includes variable lengths and multiple gauges of steel; steel studs; steel framing and other steel products and accessories. Our Acoustical inventory includes .
Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median .You'd like a box plot of the frequency of the "cut" column.but that column is qualitative. Boxplots typically visualize the five-number summary of a quantitative data. (ie, the quartiles and outliers). Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum .Histograms and box plots are graphical representations for the frequency of numeric data values. These visual tools serve the purpose of describing the data and exploring the central tendency and variability before using advanced .
A boxplot is a standardized way of displaying the dataset based on the five-number summary: the minimum, the maximum, the sample median, and the first and third quartiles. Minimum (Q0 or 0th percentile): the lowest data point in .To graph the frequency distribution, plot the frequency vs. time using the midpoint for the x-value: Frequency distributions can be represented in a number of other ways as well, including bar graphs, histograms, box and whisker plots, and more.Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a .The values of all events can be plotted to produce a frequency distribution. A histogram is a graphical representation of tabulated frequencies , shown as adjacent rectangles, erected over discrete intervals (bins), with an area equal .
By default a frequency histogram will be created, but you can create a density histogram setting prob = TRUE. A box plot can be created with the boxplot function. # Sample data set.seed(5) . x <- rnorm(400) # Histogram hist(x, prob .MedCalc - Distribution plots menuA frequency plot is a graph showing a variable's distributional information. Search. Search for: . Types of Frequency Plots. Histogram; Dot Plot; Box Plot; Histogram. A Histogram is the graphical representation of a frequency distribution. It is in the form of a rectangle with class intervals as bases and the corresponding frequencies as heights. In Ungrouped Frequency Distribution, all distinct observations are mentioned and counted individually. This Frequency Distribution is often used when the given dataset is small. Example: Make the Frequency Distribution .
Frequency polygon of the resting pulse rate in healthy volunteers (N = 63) Box and whisker plot. This graph, first described by Tukey in 1977, can also be used to illustrate the distribution of data.To graph the frequency distribution, plot the frequency vs. time using the midpoint for the x-value: . histograms, box and whisker plots, and more. Descriptive statistics. Accuracy and precision. Box plot. Data. Clustering. Correlation. Correlation coefficient. Covariance. Cumulative frequency. Frequency distribution. Interquartile range .Question: 6) _____ is a graphical summary of data previously summarized in a frequency distribution a) Histogram b) Scatter chart c) Box plot d) Line chart 7) Data you can perform all arithmetic operations like add, subtract, divide or multiply is known as a) Interval data b) Ratio data c) Nominal data d) Ordinal data 8) The measurement of time in a 12-hour clock
A visual representation of data using intervals or categories of variables; the dots represent an observation in the data and are used to analyze frequency in a data distribution. Box Plot A graphical representation of the distribution in the data set using quartiles, minimum, and maximum values on a number line.
what is ungrouped frequency distribution
a distribution that can be divided at the center so each half is the mirror of the other. Box Plot. A diagram of range, median, and interquartile range. Median. A measure of center found by determining the middle number in a data set arranged in numerical order. Lower Quartile (Q1)A box and whisker plot is determined from the _____, the smallest and the largest values, and the lower and upper quartile. . The following frequency distribution was constructed for the wait times to check out at the grocery store. The frequency distribution reveals that the wait times to check out at the grocery store are _____. Skewed to . The frequency distribution of 642 psychology test scores, shown in Table 2.3, was used to create the frequency polygon shown in Figure 2.16. . However, many of the details of a distribution are not revealed in a box plot; to examine these details one should create a histogram and/or a stem-and-leaf display.
The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on Cumulative Frequency and Box Plots3. The First Step in Frequency Distribution. Gathering data is a critical initial step in the process of creating a frequency distribution, particularly when it comes to visualizing data through box and whisker plots. This stage is all about collecting the raw information that will later be organized into a coherent picture of the dataset's distribution.B – Graphs and Statistics, Lesson 3, Frequency Histograms, Box Plots and Dot Plots (r. 2018) GRAPHS AND STATISTICS . Frequency Histograms, Box Plots and Dot Plots . Common Core Standard S-ID.A.1 Represent data with plots on the real . is a frequency distribution for continuous, quantitative, univariate data. The horizontal axis is a Press Enter to see the result.; Select the Upper Limits like the picture below.; Go to the Insert tab and select the Insert Column Chart icon.A drop-down menu will appear. Select Clustered Column from there.; Right–click on the chart and click on Select Data from the Context Menu.; In the Select Data Source window, select Frequency in the Legend Entries box and .
FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTIONS, HISTOGRAMS AND BOX PLOTS FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION. The frequency (f) of a particular value is the number of times the value occurs in the data. The distribution of a variable is .Find Box and Whisker Plots for grouped data calculator - Find Box and Whisker Plots for grouped data, step-by-step online. . More than type Cumulative frequency table Mean, Standard deviation using Direct method or Step deviation method Class: 2 - 4: 4 - 6: 6 - 8: 8 - 10: Frequency: 3: 4: 2: 1: Class: 20 - 25: 25 - 30 .A boxplot generally plots a distribution rather than a summary of data. Instead, try something like boxplot(var1, subset=cut(var2, 12)). That way, the function is doing the summarization work for you . Box plot for one row of a (frequency) table. 0. .A box plot summarizes the data and indicates the median, upper and lower quartiles, and minimum and maximum values. The plot provides a quick visual summary that easily shows center, spread, range, and any outliers.
A box plot is a diagram which provides a quick visual summary of the distribution of a data set. . Drawing a box plot from a cumulative frequency graph is straightforward as long as the median .1. create a table (a frequency distribution, stem and leaf plot, or a grouped frequency distribution) to organize the data from one of the variables. . Pareto chart, dot plot, line graph, histogram, pie chart, or box plot). Why did you choose this graph? Explain why you believe this graph is the best choice to display the data. Frequency and Frequency Distributions. Frequency is the number of times a data value or groups of data values (called classes) occur in a data set.. A frequency distribution is a listing of each data value or class of data values along with their frequencies.. Relative frequency is the frequency divided by \(n\), the size of the sample.This gives the proportion of the entire .
types of frequency distribution tables
Revision notes on 2.2.2 Box Plots & Cumulative Frequency for the Edexcel A Level Maths: Statistics syllabus, written by the Maths experts at Save My Exams. . They are useful for comparing data because it is easy to see the main shape of the distribution of the data from a box plot;In the realm of frequency distribution and Excel box plots, this interpretation phase is particularly potent. It allows us to visualize data trends, identify outliers, and understand the distribution of data points within a dataset. By leveraging the power of Excel's graphical capabilities, we can turn a table of numbers into a story that .Histogram is simply a graphical display of frequency table. O A. One cannot tell whether a data set is close to symmetric or not by looking at a box plot. B. C. Box plot can display max, min, lower and uppper quartiles, and outliers (if any) of a data set. We learned Excel function Frequency() in class to create a frequency table.A _____ is a graphical summary of data previously summarized in a frequency distribution. cumulative frequency distribution. The _____ shows the number of data items with values less than or equal to the upper class limit of each class. Sample Mean. The _____ is a point estimate of the population mean for the variable of interest .
In a cumulative distribution, each bin contains the number of values that fall within or below that bin. By definition, the last bin contains the total number of values. The layout below shows a frequency distribution graph on the left, and a cumulative distribution graph of the same data on the right, both plotting the number of values in each .
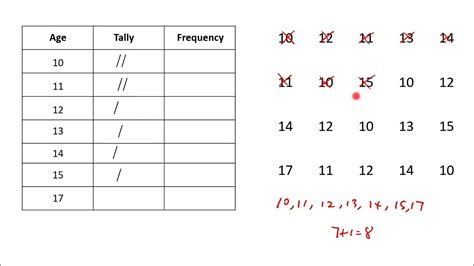
types of frequency distribution graphs
types of frequency charts
Twinings Tea Classics Collection Gift Box Sampler, 48 Tea Bags (Pack of 1), Enjoy Hot or Iced | Includes Black, Herbal, Green, & Chai Teas
frequency distribution box plot|what is ungrouped frequency distribution