box plot frequency distribution Box plots, also called box-and-whisker plots or box-whisker plots, give a good graphical image of the concentration of the data. They also show how far the extreme values are from most of the . Tuck the wires into the junction box, then align the two holes on the light fixture with the threaded posts on the plastic mounting plate. Slide the light fixture onto the posts and push firmly into .
0 · what is ungrouped frequency distribution
1 · types of frequency distribution tables
2 · types of frequency distribution graphs
3 · types of frequency charts
4 · parts of frequency distribution table
5 · frequency distribution vs relative
6 · frequency distribution graph example
7 · calculating frequency distribution
You did the right thing with dish soap. That is the first go-to lube for installing rubber and dries away harmlessly. You can also use dielectric/silicone grease which is for lubing rubber. It will remain as a lube and if that's not desired, dish soap is generally the 1st choice.
You'd like a box plot of the frequency of the "cut" column.but that column is qualitative. Boxplots typically visualize the five-number summary of a quantitative data. (ie, the quartiles and outliers). Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median .Box plots, also called box-and-whisker plots or box-whisker plots, give a good graphical image of the concentration of the data. They also show how far the extreme values are from most of the .To graph the frequency distribution, plot the frequency vs. time using the midpoint for the x-value: Frequency distributions can be represented in a number of other ways as well, including bar graphs, histograms, box and whisker plots, and more.
A box plot is a diagram which provides a quick visual summary of the distribution of a data set. It makes drawing conclusions easier and is useful for comparing two sets of data. Box plots, or box-and-whisker plots, are a visual tool used to represent the distribution of a data set. This type of graph shows key statistics of your data, including the median, quartiles, and outliers. You can use box plots . Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum .Frequency plots are helpful for monitoring the spread of continuous data. A frequency plot is a graph showing a variable’s distributional information. In other words, it summarizes the data by .
You'd like a box plot of the frequency of the "cut" column.but that column is qualitative. Boxplots typically visualize the five-number summary of a quantitative data. (ie, the quartiles and outliers).Box plots truly shine when comparing data distributions across different groups. Their compact design offers a neat summary of data, making it a breeze to compare distributional properties of the groups through the positioning of box and whisker markings. Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median would also indicate a positive skew.
Frequency distributions can be displayed in a table, histogram, line graph, dot plot, or a pie chart, to just name a few. In statistics, the frequency (or absolute frequency) of an event is the number of times the event occurred in an experiment or study. These frequencies are often graphically represented in histograms.Box plots, also called box-and-whisker plots or box-whisker plots, give a good graphical image of the concentration of the data. They also show how far the extreme values are from most of the data.To graph the frequency distribution, plot the frequency vs. time using the midpoint for the x-value: Frequency distributions can be represented in a number of other ways as well, including bar graphs, histograms, box and whisker plots, and more.
A box plot is a diagram which provides a quick visual summary of the distribution of a data set. It makes drawing conclusions easier and is useful for comparing two sets of data. Box plots, or box-and-whisker plots, are a visual tool used to represent the distribution of a data set. This type of graph shows key statistics of your data, including the median, quartiles, and outliers. You can use box plots to gain insight into some aspects of the frequency distribution of your data, including: Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.Frequency plots are helpful for monitoring the spread of continuous data. A frequency plot is a graph showing a variable’s distributional information. In other words, it summarizes the data by plotting how frequently a particular value occurs.
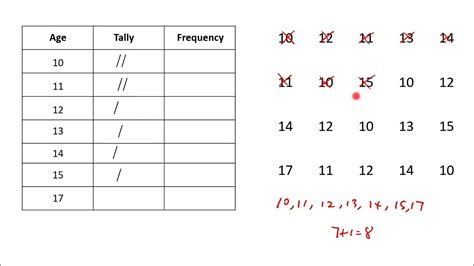
what is ungrouped frequency distribution
You'd like a box plot of the frequency of the "cut" column.but that column is qualitative. Boxplots typically visualize the five-number summary of a quantitative data. (ie, the quartiles and outliers).Box plots truly shine when comparing data distributions across different groups. Their compact design offers a neat summary of data, making it a breeze to compare distributional properties of the groups through the positioning of box and whisker markings. Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median would also indicate a positive skew.Frequency distributions can be displayed in a table, histogram, line graph, dot plot, or a pie chart, to just name a few. In statistics, the frequency (or absolute frequency) of an event is the number of times the event occurred in an experiment or study. These frequencies are often graphically represented in histograms.
Box plots, also called box-and-whisker plots or box-whisker plots, give a good graphical image of the concentration of the data. They also show how far the extreme values are from most of the data.
To graph the frequency distribution, plot the frequency vs. time using the midpoint for the x-value: Frequency distributions can be represented in a number of other ways as well, including bar graphs, histograms, box and whisker plots, and more.
A box plot is a diagram which provides a quick visual summary of the distribution of a data set. It makes drawing conclusions easier and is useful for comparing two sets of data. Box plots, or box-and-whisker plots, are a visual tool used to represent the distribution of a data set. This type of graph shows key statistics of your data, including the median, quartiles, and outliers. You can use box plots to gain insight into some aspects of the frequency distribution of your data, including:
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.

26 gauge sheet metal siding

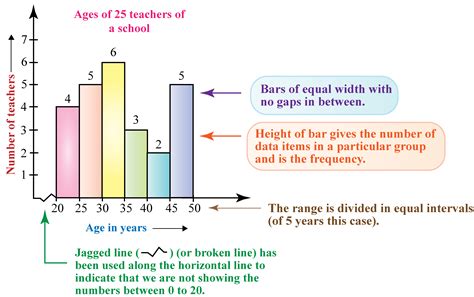
types of frequency distribution tables
For #12 metal screws, a recommended drill bit size is #12, which corresponds to a diameter of 0.2280 inches. This size falls within the range of common "#" drill bit sizes, which go from #80 through #1, with larger numbers indicating larger diameters.
box plot frequency distribution|calculating frequency distribution