box plot distribution interpretation A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value. the size of screws used in electrical boxes depends on the type of box and the gauge of the wire being used. For most applications, 10 screws are sufficient. However, if you are using thicker wire or a metal box, you may need to use 12 or 14 screws.
0 · side by boxplot interpretation
1 · how to interpret box plot results
2 · how to analyze boxplot
3 · describing box plot distribution
4 · box plot quartiles explained
5 · box plot high level summary
6 · box plot distribution shapes
7 · box plot diagram labelled
Discover the key skills that are required for a Metal Fabricator to succeed. MIG, Hand Tools, Aluminum skills are good to have on your resume.
What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot .
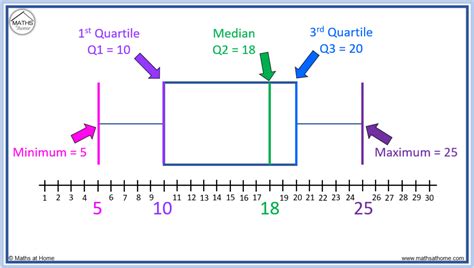
A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.Understanding how to interpret box plots can provide valuable insights into the variability and distribution of a dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the key components of box plots and show you how to interpret . What is a Box Plot? A box plot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a dataset based on a five-number summary: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3),.
A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.
side by boxplot interpretation
What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.
Understanding how to interpret box plots can provide valuable insights into the variability and distribution of a dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the key components of box plots and show you how to interpret them effectively. What is a Box Plot? A box plot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a dataset based on a five-number summary: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3),.A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.A box plot is a diagram used to display the distribution of data. A box plot indicates the position of the minimum, maximum and median values along with the position of the lower and upper quartiles. From this, the range, interquartile range and skewness of the data can be observed.
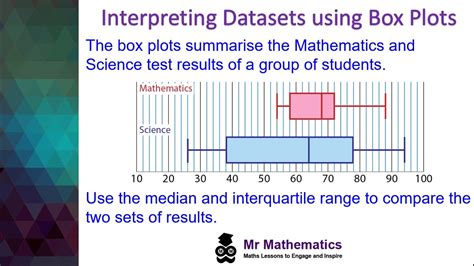
Examine your boxplot to look at the center and spread of your data and compare differences between grouping variables within your data. Examine the median, the interquartile box, and identify outliers as you interpret the distribution of your data. Examine the .
A boxplot, also called a box and whisker plot, is a graph that shows the dispersion and central tendency of a dataset using a five number summary. The dispersion — a measure of how spread out a data set is — includes quartiles and the interquartile range. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”
A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.Understanding how to interpret box plots can provide valuable insights into the variability and distribution of a dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the key components of box plots and show you how to interpret them effectively.
What is a Box Plot? A box plot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a dataset based on a five-number summary: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3),.A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.A box plot is a diagram used to display the distribution of data. A box plot indicates the position of the minimum, maximum and median values along with the position of the lower and upper quartiles. From this, the range, interquartile range and skewness of the data can be observed.Examine your boxplot to look at the center and spread of your data and compare differences between grouping variables within your data. Examine the median, the interquartile box, and identify outliers as you interpret the distribution of your data. Examine the .
how to interpret box plot results
Electrical box screw size for junction boxes. Junction boxes usually use a heavier duty screw, an 8-32. Junction boxes often hold heavier light fixtures, so they need a screw that can hold a bit more weight. 8-32 is a very common size, at least. An 8-32 is .164 inches in diameter, which is a shade over 5/32.
box plot distribution interpretation|box plot high level summary